
30 of the Best Dietary Sources of Vitamin D Vitamin d rich food, Iodine rich foods, Vitamin d
1. Pasture-Raised Lard 2. Salmon 2. Atlantic Mackerel 3. Oysters 5. Egg yolks 6. Various Other Fish Foods High In Vitamin D: The Bottom line What is Vitamin D? Vitamin D is both a nutrient we eat and a hormone that our bodies produce when exposed to ultraviolet-B rays from the sun. That's why it's often called the "sunshine vitamin."
Lard is Packed with Vitamin D Coast Packing Company
According to Mary Enig, author of Know Your Fats, lard is about 40 percent saturated, 50 percent monounsaturated, and contains 10 percent polyunsaturated fatty acids. It is also one of our richest dietary sources of vitamin D.
Lard vs. Butter — InDepth Nutrition Comparison
Lard is heart-healthy "Lard is an animal fat, and it is high in saturated fat and cholesterol. Doesn't that mean it raises my risk for heart disease?" The pervasive myth that animal fats increase the risk of heart disease is just that - a myth.

What foods have the most Vitamin D? Infographics
Lard is high in Vitamin D. It has about 1000 IU (international units) per tablespoon depending on what they are fed and how much sunlight the animals get. Our pigs are raised under ideal conditions- in the open air and sunshine, for high doses of vitamin D! More Vitamin D means less seasonal mood swings, sounds good to me!

How to Render Lard from Pastured Pigs Real food recipes, Food, Lard recipe
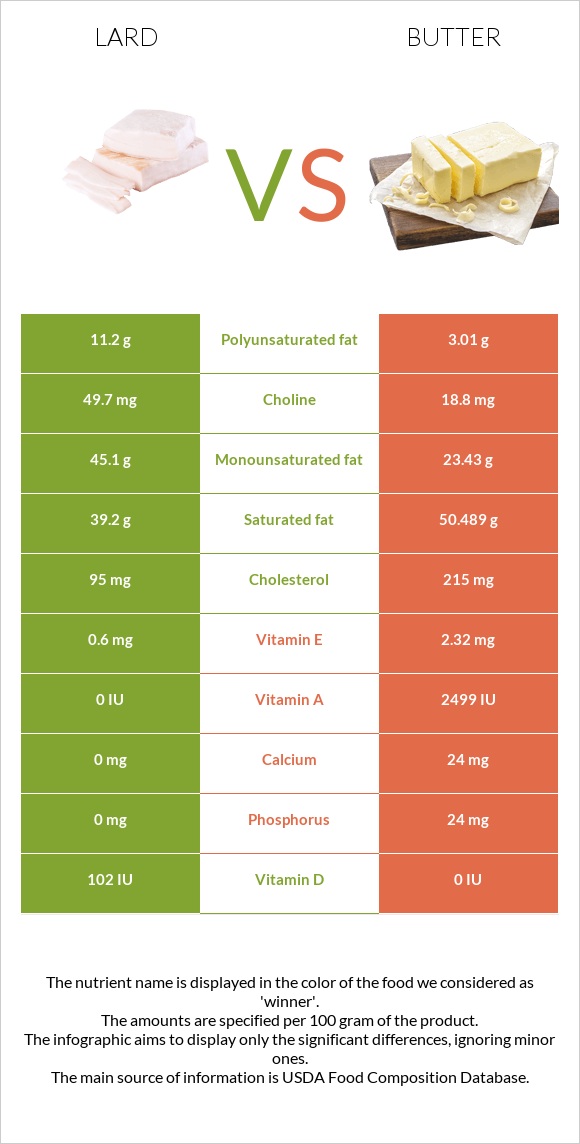
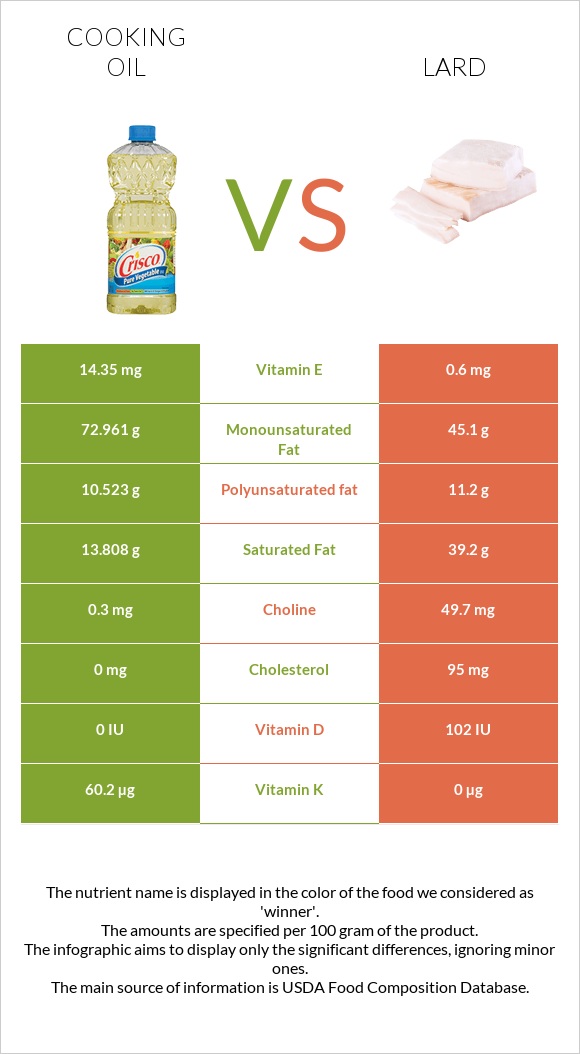
100 grams of Lard contains 2.5 micrograms of Vitamin D, that's the 25% of the daily recommended value for an adult. Vitamin E. 0.6 mg. The American Heart Association recommends obtaining health benefits of vitamin E antioxidant. Vitamin E is a group of eight compounds called tocopherols and tocotrienols which reduces cholesterol and the risk.

Misunderstood Vitamin D, Lard, and Cholesterol Cholesterol Part 3 Health Unlimited
Coast Packing: Lard is Packed with Vitamin D If you're like most people in the industry, you love lard for the flavor it imparts to popular dishes. It's the difference-maker in refried beans, tortillas, tamales, carnitas and scads of other offerings that make Mexican food so special.

Rendering Homegrown Lard...Vitamin D Rich! YouTube
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin available via ultraviolet rays (mainly the sun), a few foods and supplements. Vitamin D's main purpose is to regulate calcium and phosphate to keep your bones.

Pin on Low Carb Keto Living
Vitamins and Minerals Lard is not a significant source of vitamins or minerals. However, lard from pigs raised on pasture can be high in fat-soluble vitamins D and K2. There is more information on this later. Key Point: Lard is a source of dietary fat, and it may also provide vitamins D and K2. Is Frying With Lard Healthy?

The Importance of Vitamins A and D Nutrients You Must Have Selene River Press
Lard (yes, pig fat) is one food that many point to as packed with vitamin D. Is lard your vitamin D ticket? No. Lard has very small levels of vitamin D even if the pig is eating grass. I discuss the issue in the video below (or jump over to YouTube for a gander here ). Your very best source of vitamin D is still sunlight.

VITAMIN D 16 Health Benefits and 15 Vitamin D Rich Foods Ecosh
Vitamin D — Lard is the #2 food source for vitamin D, only trailing cod liver oil. One tablespoon actually contains 1,000 IUs! Heat Stable — Pork fat isn't destabilized by higher heat. This means it's much healthier and less of a cancer risk than other oils that smoke at high temperatures.

Vitamin D Deficient in America? Eat Lard! Selene River Press
1. Lard Is Easy On Your Wallet (And Your Body) We all have this perception that cheap foods are not good for your body. Take ramen noodles for example. But it's not the case for lard. Lard packs a lot of health benefits without punching your wallet. That is a rarity nowadays. We wonder why so much of America is overweight.

Lard made from pastured hogs is an excellent source of Vitamin D. The only real food better for
Lard is commonly used in baking for creating flaky pastries, frying foods to achieve crispiness, adding richness to gravies and sauces, and as an essential ingredient in traditional dishes like tamales and tortillas. Nutritional composition of lard. Lard contains high amounts of trans fat, cholesterol, and nutrients such as choline and vitamin D.

the handshake — jam, cream, lard, vitamin d, tinfoil, lunchbox...
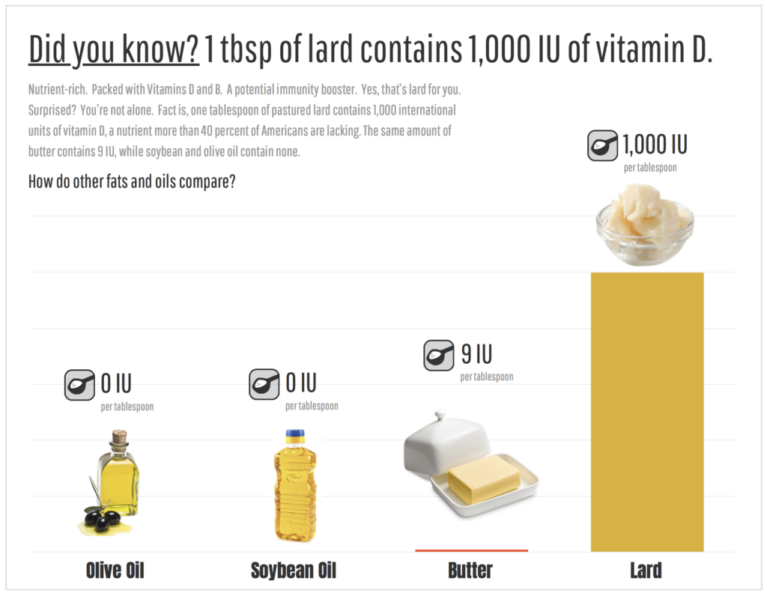
Packed with Vitamins D and B, it's a potential immunity booster. Fact is, one tablespoon of lard contains 1,000 international units of vitamin D, a nutrient more than 40 percent of Americans are lacking. The same amount of butter contains 9 IU, and olive oil contains none. Scientists actually rank lard #8 out of the100 most nutritious foods.

Rendered Pork Lard Botany Bay Farm
What is Lard? Lard is pork fat. There are two types you can get for making lard. Leaf lard and back fat. Leaf lard is the fat around the kidneys and is considered the best type of fat for making lard. It has a very neutral flavor and is ideal for baking purposes. The back fat is also acceptable though some say it renders a stronger pork flavor.
Olive oil vs. Lard — InDepth Nutrition Comparison
More From Prevention Is lard healthy or unhealthy? Lard is primarily a fat source, and has basically zero protein or carbohydrates. But despite what you might have heard about fats, this is.

6 Reasons to Add Lard to Your Diet
Vitamin D: A tablespoon of lard from pasture-raised pigs has about 1,000 IU of vitamin D, and by comparison, 1 tablespoon of butter has 9 IU of vitamin D, while the same amount of olive oil has none. Lard is one of the highest dietary sources of vitamin D, and about 42% of U.S. adults have been found deficient in this vitamin .